前缀树、链表相关题目
前缀树
- 前缀树又名字典树,单词查找树,Trie树,多路树形结构,和hash效率有一拼,是一种用于快速检索的多叉树结构。多用于词频搜索或者模糊查询。
- 查询时只与样本长度有关,而与样本量无关。
- 1)单个字符串中,字符从前到后的加到-棵多叉树上
2)字符放在路上,节点上有专属的数据项(常 见的是pass和end值)
3)所有样本都这样添加,如果没有路就新建,如有路就复用
4)沿途节点的pass值增加1,每个字符串结束时来到的节点end值增加1
可以完成前缀相关的查询
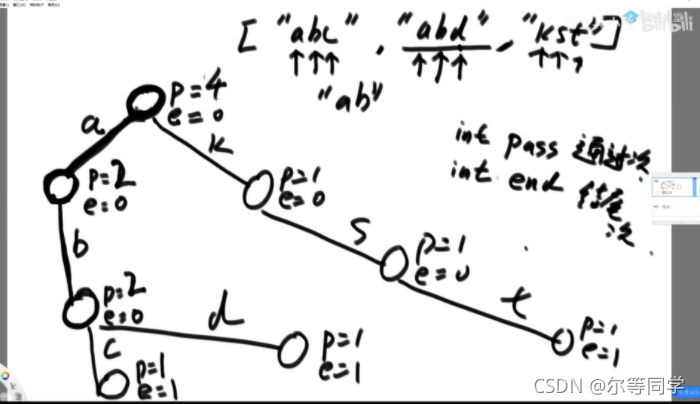
pass 为通过次数,end 为以当前元素结尾的次数
生成这棵树的代价为 O(N)
public class Code_01_TrieTree {
public static class TrieNode {
public int path;
public int end;
public TrieNode[] nexts;
public TrieNode() {
path = 0; //有多少个结点到达过
end = 0; //有多少个字符串以这个结点结尾
nexts = new TrieNode[26]; //通向子节点的路,如果题目所给的范围不确定就用map
}
}
public static class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
public Trie() {
//准备一个头结点
root = new TrieNode();
}
//将一个单词插入
public void insert(String word) {
if (word == null) {
return;
}
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = chs[i] - 'a';
if (node.nexts[index] == null) {
node.nexts[index] = new TrieNode();
}
node = node.nexts[index];
node.path++;
}
node.end++;
}
//在结构中删除这个单词
public void delete(String word) {
if (search(word) != 0) {
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = chs[i] - 'a';
if (--node.nexts[index].path == 0) {
//如果某个结点-1之后==0,则说明此节点之后的结点也是-1之后==0,因此直接=null即可。
node.nexts[index] = null;
return;
}
node = node.nexts[index];
}
node.end--;
}
}
//查找某个单词插入了几次
public int search(String word) {
if (word == null) {
return 0;
}
char[] chs = word.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = chs[i] - 'a';
if (node.nexts[index] == null) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts[index];
}
return node.end;
}
//查某个字符串前缀数量是多少
public int prefixNumber(String pre) {
if (pre == null) {
return 0;
}
char[] chs = pre.toCharArray();
TrieNode node = root;
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chs.length; i++) {
index = chs[i] - 'a';
if (node.nexts[index] == null) {
return 0;
}
node = node.nexts[index];
}
return node.path;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie trie = new Trie();
System.out.println(trie.search("zuo"));
trie.insert("zuo");
System.out.println(trie.search("zuo"));
trie.delete("zuo");
System.out.println(trie.search("zuo"));
trie.insert("zuo");
trie.insert("zuo");
trie.delete("zuo");
System.out.println(trie.search("zuo"));
trie.delete("zuo");
System.out.println(trie.search("zuo"));
trie.insert("zuoa");
trie.insert("zuoac");
trie.insert("zuoab");
trie.insert("zuoad");
trie.delete("zuoa");
System.out.println(trie.search("zuoa"));
System.out.println(trie.prefixNumber("zuo"));
}
}
链表
笔试可以不在意空间复杂度,一切为了时间复杂度
面试时,时间复杂度最重要,但要节省空间
::快慢指针::
1)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点,偶数长度返回上中点
2)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点,偶数长度返回下中点
3)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点前一个,偶数长度返回.上中点前一个
4)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点前一个,偶数长度返回下中点前一个.
1)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点,偶数长度返回上中点
static class Node{
int val;
Node next;
}
public static Node mid0rUpMidNode(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return head;
}
//
Node slow = head.next;
Node fast = head. next. next;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow. next;
fast = fast .next .next;
}
return slow;
}
public static Node mid0rUpMidNode2(Node head) {
if (head == null|| head.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node n1 = head;
Node n2 = head;
while (n2.next != null && n2.next.next != null) { // find mid node
n1 = n1.next; // n1 -》mid
n2 = n2.next.next; // n2 -> end
}
return n1;
}
2)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点,偶数长度返回下中点
public static Node mid0rDownMidNode (Node head) {
if (head == null|| head.next == null) {
return head;
}
Node slow = head . next;
Node fast = head . next;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next .next;
}
return slow;
}
3)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点前一个,偶数长度返回.上中点前一个
public static Node mid0rUpMidPreNode(Node head) {
if (head == null|| head.next == null|| head.next.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head. next. next;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast .next .next;
}
return slow;
}
4)输入链表头节点,奇数长度返回中点前一个,偶数长度返回下中点前一个.
public static Node mid0rUpMidPreNode(Node head) {
if (head == nu11|| head.next == nu11|| head.next.next == nu1l) {
return nu1l;
}
Node slow = head;
Node fast = head . next. next;
while (fast.next != nu1l && fast.next.next != nu1l) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast .next .next;
}
return slow;
}
::给定一个单链表的头节点head,请判断该链表是否为回文结构。::
1)哈希表方法特别简单(笔试用)
2)改原链表的方法就需要注意边界了( 面试用)
利用栈,先遍历一遍压栈,然后在遍历一遍,同时与栈顶元素对比
用更少的空间?
快慢指针求出中点,和上中点
将后半部分压栈,再次出栈与前半部分对比
常数空间?
先快慢指针定位中点和末尾,将中点的next指针指向null
将后半部分指针逆序,然后头尾依次对比,当有一个的指针指向为null,即为回文结构
中间有一个不一样则为非回文
注意返回结果前,需要把后半部分逆序回来.
将单向链表按某值划分成左边小、中间相等、右边大的形式
1)把链表放入数组里,在数组上做partition (笔试用)
2)分成小、中、大三部分,再把各个部分之间串起来(面试用)
public static Node listPartition2(Node head, int pivot) {
Node sH = nu1l; // small head
Node sT = nu1l; // small tail
Node eH = nu1l; // equal head
Node eT = nu1l; // equal tail
Node mH = nu11; // big head !
Node mT = nu1l; // big tail
Node next = nu1l; // save next node
// every node distributed to three lists
while (head != nu1l) {
next = head.next;
head.next = nu1l;
if (head.value < pivot) {
if (sH == null) {
sH = head;
sT = head;
} else{
sT .next = head;
sT = head;
}else if (head.value == pivot) {
if (eH == nu11) {
eH = head;
eT = head;
} else {
eT.next = head;
eT = head;
}
}
head= next;
}
if (sT != null) { //如果有小」<域
sT .next = eH;
eT= eT==null?sT:eT;//谁去连大于区域的头,谁就变成eT
}
// 上面的if, 不管跑了没有,et
// all reconnect
if (eT != null) { //如果小于以域和等门<规,不是都没有
eT .next = mH;
}
return sH!=null?sH:(eH!=nu1l?eH:mH);
}
拷贝有特殊指针的链表
-种特殊的单链表节点类描述如下
class Node {
Int value.
Node next:
Node rand;
Node(int val)
}
rand指针是单链表节点结构中新增的指针,rand可 能指向链表中的任意一个节点,也可能指向mull.
给定一个由ndoe节点类型组成的无环单链表的头节点head.请实现一个函数完成这个链表的复制 并返回复制的新链表的头节点。
[要求]
时间复杂度ON).额外空间复杂度O(1)
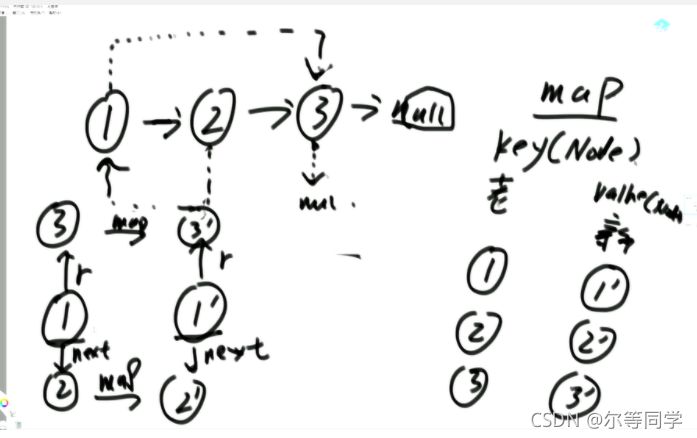
建立map
第一遍遍历, key为老节点,value 为新的节点
第二遍遍历链表, 由老节点找到新的节点,并将rand指针赋值给新的节点
最后返回 新节点
public static Node copyListWi thRand1(Node head) {
HashMap<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
Node cur = head;
while (cur != nu1l) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur .value));
cur = cur .next ;
}
cur = head;
while (cur != nu1l) {
.//cur七
// map.get(cur) 新
map.get(cur).next = map. get(cur . next);
map. get(cur).rand = map.get(cur.rand);
cur = cur .next;
}
return map. get(head);
}
不用hash 表 ,实现拷贝
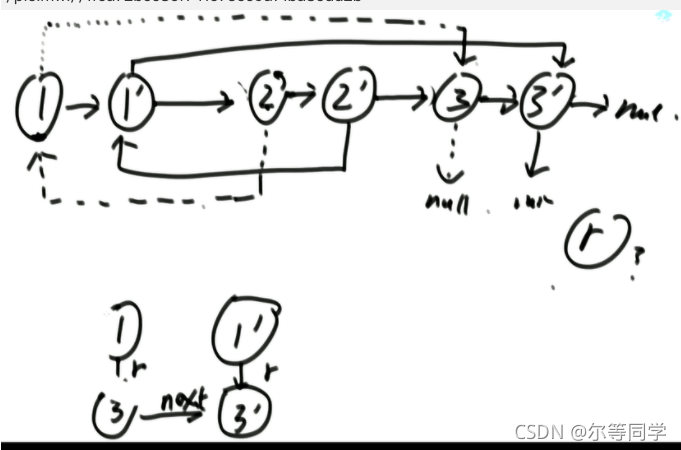
第一次遍历,建立新的节点插入到老节点的后方
第二次遍历设置rand指针,
如果1的rand指向 ---> 3
则 3的拷贝节点就在 3后方
将 1的拷贝节点的rand 指针指向3 的后一个节点
最后再将拷贝的节点串联起来返回其头节点
public static Node copyListWithRand2(Node head) {
if (head == nu1l) {
return null;
}
Node cur = head;
Node next = null;
// copy node and link to every node
//1->2
//1-> 1’->2
while (cur != nu11) {
//cur老|
next = cur .next;
cur .next = new Node(cur .value);
cur .next.next = next;
cur = next;
cur = head;
}
Node curCopy = nu1l;
// set copy node rand
//1->1’->2->2'
while (cur != nu1l) {
// cur 2
// cur.next 新copy
next = cur .next .next;
curCopy = cur . next;
curCopy.rand = cur .rand != null ? cur.rand.next : null;
cur = next;
}
// head head.next
Node res = head.next; .
cur = head;
// split
while (cur != nu1l) {
next = cur .next. next;
curCopy = cur .next;
cur .next = next;
curCopy.next = next != nu1l ? next.next : nu11;
cur = next;
}
return res;
}
返回相交的第一个节点
给定两个可能有环也可能无环的单链表,头节点head1和head2。请实现一个函数,如果两个链表相交,请返回相交的第一个节点。如果不相交,返回null。
[要求]
如果两个链表长度之和为N,时间复杂度请达到O(N),额外空间复
杂度请达到0(1)。
给一个有环链表,找出其入环的节点
//找到链长第个入坏官点。如果无坏。这null
public static Node getLoopNode(Node head) {
if (head == nu11 | head.next == nu11|| head.next.next == nu11) {
return nu11;
}
//n1性n2快
Node n1 = head.next; // n1 -> slow
Node n2 = head.next.next; // n2 -> fast
while (n1 != n2) {
if (n2.next == null|| n2.next.next == nu1l) {
return nu11;
}
n2 = n2.next .next;
n1 = n1.next;
}
n2 = head; // n2 -> walk again from head
while (n1 != n2) {
n1 = n1.next;
n2 = n2.next; .
}
return n1;
}
两条链表都无环
第一条链表节点都入set,第二条链表查,查到重复即为相交节点
不用set
遍历第一条链表,记录最后一个节点,且记录链表长度 (长度记作x)
遍历第二条链表,记录最后一个节点,且记录链表长度 (长度记作y)
如果两个最后节点不同,则不相交
x 与y
大的 先开始走, 走x-y步
然后两条链表一起走, 会在相交的节点相遇
//如果两个链长都无坏,驱回第:个相父节点,如果不想灾。驱null
public static Node noLoop(Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 == null |I head2 == null) {
return nu11;
}
Node cur1 = head1;
Node cur2 = head2;
intn=0;
while (cur1.next != nu1l) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2.next != nu1l) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
if (cur1 != cur2) {
return nu1l;
}
// n :链长1长度减大链 长2长度的值
cur1=n>0?headl:head2;//谁长,谁的头变成cur1
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1; //谁知,谁的头变成cur2
while(n1=){
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next;
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
return cur1;
}
一个有环,一个无环,这种情况,两条链表不相交
两个都有环
如果两个有环链表相交,那他们一定是共用这个环
一共有三种情况
如果loop1 的内存地址等于loop2 的内存地址
则为第二种情况
如果loop 1 不等于 loop 2
让loop1 沿着环走,如果没有遇到 loop2 则为第一种情况
也就是没有相交
如果遇到了loop2 就是第三种情况

//两个有环链化。返网第.个相交节点。如果不想交题川null
public static Node bothLoop(Node head1, Node 1oop1, Node head2, Node 1oop2) {
Node curl = nu1l;
Node cur2 = null;
if (loop1 == 1oop2) {
cur1 = head1 ;
cur2 = head2;
intn=0;
while (cur1 != 1oop1) {
n++;
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
while (cur2 != 1oop2) {
n--;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
cur1=n》0?head1:head2;
cur2 = cur1 == head1 ? head2 : head1;
n = Math.abs(n);
while (n != 0) {
n--;
cur1 = cur1.next ;
}
while (cur1 != cur2) {
cur1 = cur1.next;
cur2 = cur2.next;
}
}else {
cur1 = 1oop1.next;
while (cur1 != 1oop1) {
if (cur1 == 1oop2) {
return loop1;
}
cur1 = cur1.next;
}
return nu11;
}
主方法
public static Node getIntersectNode (Node head1, Node head2) {
if (head1 = null|| head2 = null) {
return nu11;
Node 1oop1 = getLoopNode(head1);
Node_ 1oop2 = getL oopNode (head2) ;
if (loop1 == nu11 && loop2 == nu11) {
return noloop(head1, head2);
}
if (loop1 != nu1l && loop2 != nu11) {
return bothLoop(head1, loop1, head2, 1oop2);
}
return null;
}
能不能不给单链表的头节点,只给想要删除的节点,就能做到在链表上把这个点删掉?
抖机灵
将删除节点的下一个结点的值赋值给删除节点,然后将next指向下一个节点的下一个节点
但不能删除最后一个节点